Comparatif / Superlatif
📝 Mini-cours GRATUIT
Le superlatif
🍀 Fiches de révision PREMIUM
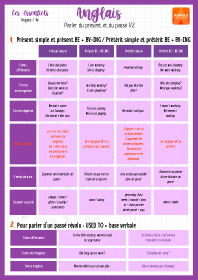
Parler du présent et du passé
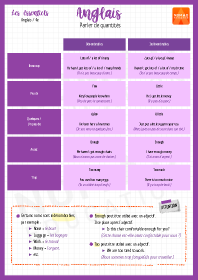
Parler de quantités

Le passif – Les conseils – L’hypothèse
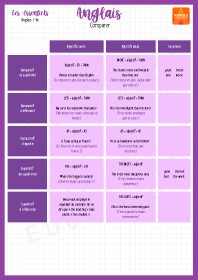
Comparer

Parler du présent et du passé

Parler de quantités

Le passif – Les conseils – L’hypothèse

Comparer