Définition
La projection orthogonale d'un point M sur une droite (d) est le point H d'intersection de la droite (d) et de la perpendiculaire à (d) passant par M.
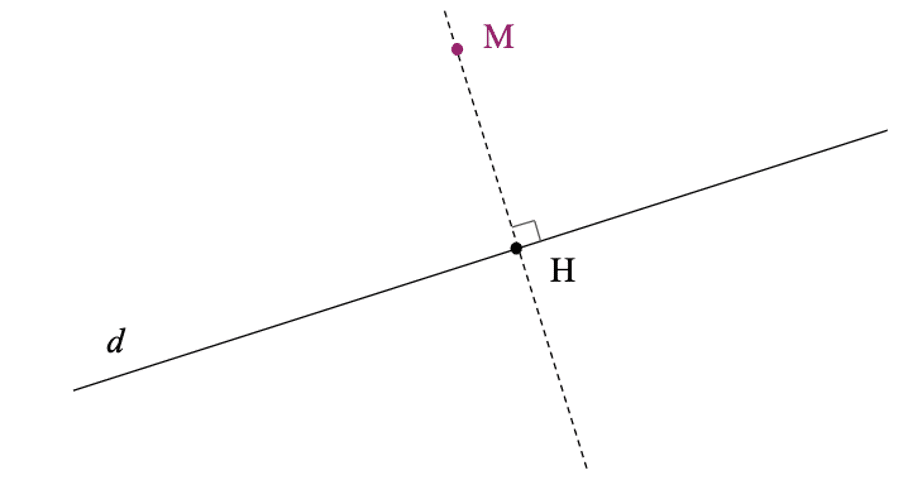
H est le projeté orthogonal du point M sur la droite (d).
Propriétés
- Le projeté d'un segment est un segment qui peut être réduit à un point.
- Le milieu d'un segment se projette au milieu du segment image.
Repérage dans le plan
- Coordonnées du milieu d'un segment
Soient A(xA ;yA);B(xB ;yB) et M(xM ;yM)
Si M est le milieu du segment [AB] alors :
xM=xA+xB2 et yM=yA+yB2 - Carré de la distance entre 2 points
Soient A(xA ;yA) et B(xB ;yB) alors :
AB2=(xB−xA)2+(xB−yA)2